Kicking off with Understanding asset classes, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone for a high school hip style that will keep you hooked till the end. Asset classes are like the different squads in the investment game, each bringing its unique strengths and weaknesses to the table. Let’s dive in and uncover the secrets behind these financial players!
As we explore the world of asset classes, you’ll discover the key to unlocking a diverse and rewarding investment portfolio. Get ready to level up your financial knowledge and make informed decisions like a boss!
Definition of Asset Classes
Asset classes refer to different categories of investments that share similar characteristics and behave in a particular way in the financial markets. Understanding asset classes is crucial for investors as it helps in diversifying their portfolios and managing risk effectively.
Main Types of Asset Classes
- Cash Equivalents: These are low-risk, short-term investments that include Treasury bills, certificates of deposit, and money market funds.
- Fixed-Income Securities: Also known as bonds, these investments provide a fixed income stream over a period of time and include government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds.
- Equities: Commonly referred to as stocks, equities represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for capital appreciation through share price increases and dividends.
- Real Estate: Investments in physical properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial real estate, as well as real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Commodities: These include physical goods such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products, and are often used as a hedge against inflation.
Importance of Understanding Asset Classes in Investment
Investors need to understand asset classes to build a well-diversified portfolio that can weather market fluctuations and economic uncertainties. By allocating investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce overall risk and potentially enhance returns. Additionally, knowledge of asset classes helps investors align their investment goals with their risk tolerance and time horizon, leading to a more strategic and successful investment approach.
Common Types of Asset Classes
When it comes to investing, asset classes play a crucial role in determining the risk and return characteristics of a portfolio. There are traditional asset classes that most investors are familiar with, as well as alternative asset classes that offer unique opportunities.
Traditional Asset Classes
- Stocks: Also known as equities, stocks represent ownership in a company. They offer the potential for high returns but also come with higher volatility.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They are considered lower risk than stocks and provide a steady stream of income through interest payments.
- Cash and Cash Equivalents: This category includes money market funds and savings accounts. They are the safest asset class but offer lower returns compared to stocks and bonds.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments involve properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial. They can provide rental income and potential appreciation in value.
Alternative Asset Classes
- Private Equity: Private equity involves investing in privately held companies. This asset class can offer high returns but is illiquid and requires a long-term commitment.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds use a variety of strategies to generate returns for investors. They often have higher fees and are only available to accredited investors.
- Commodities: Commodities include physical goods such as gold, oil, and agricultural products. They can provide diversification benefits and act as a hedge against inflation.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have gained popularity as an alternative asset class. They are highly volatile and speculative in nature.
Risk and Return Profiles, Understanding asset classes
When comparing different asset classes, it’s important to consider the risk and return profiles. Generally, higher risk assets have the potential for higher returns, but they also come with increased volatility and the possibility of significant losses. On the other hand, lower risk assets may offer more stability but lower returns over the long term. It’s crucial for investors to diversify their portfolios across various asset classes to mitigate risk and achieve their financial goals.
Characteristics of Each Asset Class: Understanding Asset Classes
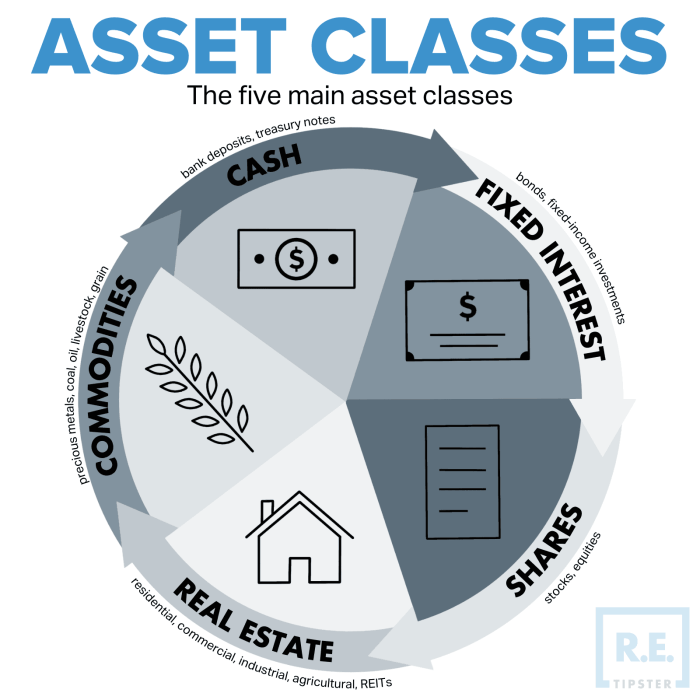
Equities, fixed-income securities, and real estate investments each have unique characteristics that make them attractive to investors. Let’s explore the key features of each asset class.
Equities
Equities, or stocks, represent ownership in a company. Key features of equities include:
- Potential for high returns: Stocks have the potential to offer high returns over the long term, making them attractive for growth-oriented investors.
- Risk and volatility: Equities are known for their risk and volatility, as stock prices can fluctuate significantly in the short term.
- Dividends: Some stocks pay dividends to shareholders, providing a source of income in addition to capital appreciation.
- Liquidity: Stocks are generally liquid assets, meaning they can be easily bought and sold on the stock market.
Fixed-Income Securities
Fixed-income securities, such as bonds, are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, or other entities. Characteristics of fixed-income securities include:
- Income generation: Bonds pay interest at a fixed rate, providing a predictable income stream for investors.
- Principal protection: Bonds typically have a maturity date at which the principal amount is repaid, offering a level of capital protection.
- Lower risk: Fixed-income securities are generally considered less risky than equities, offering more stability in volatile markets.
- Interest rate sensitivity: Bond prices are sensitive to changes in interest rates, with prices typically falling when rates rise.
Real Estate Investments
Real estate investments involve purchasing properties, such as residential or commercial real estate, to generate income or appreciation. Unique aspects of real estate investments include:
- Tangible asset: Real estate is a tangible asset that provides intrinsic value through physical properties like land and buildings.
- Income potential: Real estate can generate rental income, offering a steady cash flow for investors.
- Appreciation: Real estate values have the potential to appreciate over time, providing capital gains for investors.
- Diversification: Real estate investments can help diversify a portfolio, reducing overall risk through exposure to different asset classes.
Factors Influencing Asset Class Performance
When it comes to understanding asset class performance, various factors play a significant role. Economic indicators, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment all have a direct impact on how different asset classes behave in the market.
Economic Indicators Impact
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and unemployment levels can greatly influence asset class performance. For example, a strong GDP growth can boost the stock market as companies are expected to perform well. Conversely, high inflation rates may lead to a decrease in the value of bonds as investors seek higher returns to offset the loss in purchasing power.
Geopolitical Events Influence
Geopolitical events like wars, trade disputes, elections, and natural disasters can have a significant impact on asset class performance. For instance, uncertainty surrounding a trade war between two major economies can lead to market volatility and negatively affect stock prices. On the other hand, geopolitical stability in a region can attract foreign investments and boost the real estate market.
Role of Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment, or how investors feel about the market, plays a crucial role in determining asset class performance. Positive sentiment can drive up stock prices as investors are optimistic about the future prospects of companies. Conversely, negative sentiment can lead to a sell-off in stocks and a shift towards safer assets like gold or treasury bonds.