Yo, get ready to dive into the world of Asset allocation strategies! This topic is all about making those money moves and securing those bags. So, buckle up and let’s roll!
Now, let’s break it down for you – from the basics to the nitty-gritty details, we’ve got you covered.
Asset Allocation Strategies
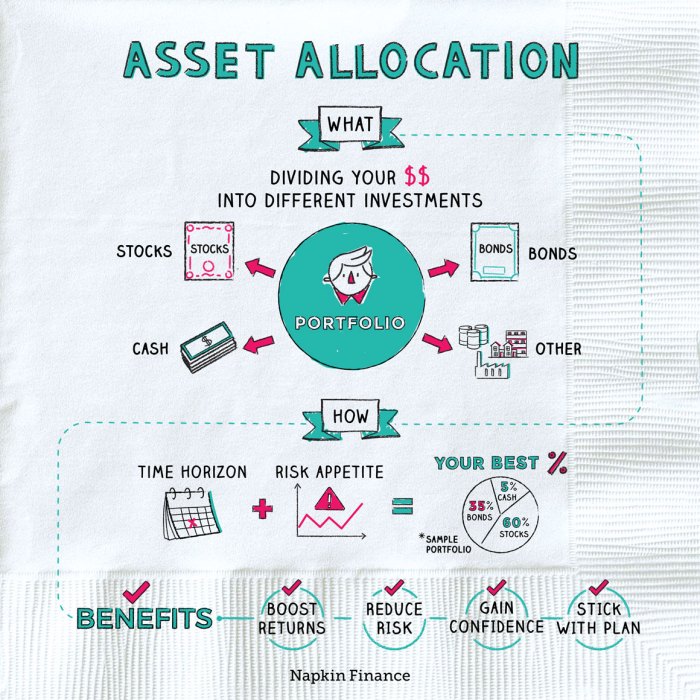
Asset allocation is the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to achieve a specific investment goal.
Asset allocation is crucial in investment because it helps manage risk by spreading investments across different asset classes that may react differently to market changes. This diversification can help reduce the overall volatility of the portfolio and potentially improve returns over the long term.
Examples of Different Asset Classes
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Represent debt issued by a corporation or government and provide steady income with lower risk compared to stocks.
- Cash Equivalents: Include assets like money market funds or certificates of deposit that offer stability and liquidity but lower returns.
Impact of Asset Allocation on Risk Management
Asset allocation plays a crucial role in risk management as it helps investors balance the risk and return potential of their portfolios. By diversifying across different asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market fluctuations on their overall investment performance. It allows them to mitigate the risk of a significant loss in any single asset class by spreading their investments across various types of assets. This strategy helps investors achieve a more stable and consistent return over time.
Traditional vs. Modern Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to asset allocation strategies, there are two main approaches: traditional and modern. Let’s dive into the key differences between these two methods.
Role of Diversification
One of the fundamental principles of asset allocation is diversification, which involves spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk. Traditional strategies typically focus on a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash, while modern approaches may incorporate alternative investments like real estate, commodities, or cryptocurrencies.
Technology’s Influence
Technology has revolutionized modern asset allocation strategies by providing access to sophisticated tools and algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time. Robo-advisors and AI-driven platforms have made it easier for investors to create and manage diversified portfolios efficiently.
Examples of Allocation Models
- Traditional Model: The 60/40 portfolio, which consists of 60% stocks and 40% bonds, is a classic example of a traditional asset allocation strategy.
- Modern Model: The Risk Parity strategy, which aims to balance risk across different asset classes rather than focusing solely on returns, is a popular modern approach to asset allocation.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation is a long-term investment strategy that involves setting target allocations for various asset classes based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. The main objective of strategic asset allocation is to create a diversified portfolio that aligns with your financial objectives while managing risk effectively.
Long-term Focus of Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation focuses on maintaining a consistent investment approach over a long period, typically spanning several years. By establishing a strategic asset allocation plan, investors aim to capitalize on the long-term growth potential of different asset classes while minimizing the impact of short-term market fluctuations.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with your long-term financial goals.
- Consider the impact of inflation and market trends on your investment strategy to make informed decisions.
- Stay committed to your strategic asset allocation plan, even during market volatility, to benefit from compounding returns over time.
Impact of Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals
Your risk tolerance and investment goals play a crucial role in determining the asset allocation mix that suits your financial needs. Higher risk tolerance may allow for a more aggressive allocation towards equities, while conservative investors may prefer a higher allocation to fixed income securities.
It is essential to strike a balance between risk and return based on your personal financial situation and investment preferences.
- Assess your risk tolerance through various factors such as investment experience, financial goals, and time horizon.
- Align your asset allocation with your investment goals, whether it’s capital preservation, growth, income generation, or a combination of these objectives.
- Seek professional advice or use online tools to determine the optimal asset allocation mix that fits your risk profile and objectives.
Tips for Creating a Strategic Asset Allocation Plan
Developing a strategic asset allocation plan requires careful consideration of your financial circumstances and investment preferences. Here are some tips to help you create an effective plan:
- Evaluate your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon before determining your target asset allocation.
- Diversify your portfolio across different asset classes to reduce risk and enhance potential returns.
- Regularly monitor and adjust your asset allocation in response to changing market conditions or life events that may impact your financial goals.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to a portfolio’s asset allocation to take advantage of market opportunities or to manage risks. Unlike strategic asset allocation, which focuses on long-term goals, tactical asset allocation is more about reacting to current market conditions.
Purpose of Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation aims to enhance portfolio returns by exploiting short-term market inefficiencies or trends. It allows investors to capitalize on immediate opportunities or protect their investments from potential downturns.
- Allocating more funds to sectors or asset classes that are expected to outperform in the short term.
- Reducing exposure to areas that are predicted to underperform or face potential risks.
- Responding quickly to changing market conditions to optimize returns and manage volatility.
Short-term Nature of Tactical Asset Allocation Decisions
Tactical asset allocation decisions are typically made within a shorter time frame, often weeks or months, compared to strategic asset allocation decisions that are made for the long term. This agility allows investors to adapt swiftly to market shifts and take advantage of emerging opportunities.
Role of Market Conditions in Tactical Asset Allocation Strategies
Market conditions play a crucial role in guiding tactical asset allocation strategies. Investors analyze economic indicators, market trends, geopolitical developments, and other factors to make informed decisions on adjusting their portfolio allocations.
For example, if there is a sudden increase in interest rates, investors may choose to reduce their exposure to interest rate-sensitive assets like bonds and increase allocations to sectors that benefit from higher rates, such as financials.
Examples of Tactical Asset Allocation Techniques
- Market Timing: Making decisions based on short-term market forecasts or technical indicators.
- Factor Rotation: Rotating between different factors like value, growth, or momentum depending on market conditions.
- Sector Rotation: Shifting allocations among sectors to capitalize on sector-specific trends or opportunities.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation involves regularly adjusting the allocation of investment assets in a portfolio based on changing market conditions. This strategy aims to optimize returns and manage risk by shifting investments between different asset classes as market conditions evolve.
Characteristics of Dynamic Asset Allocation
- Actively managed approach to asset allocation
- Responsive to market trends and economic indicators
- Frequent adjustments to investment allocations
- Emphasis on maximizing returns and managing risk
Benefits of Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation allows investors to take advantage of changing market conditions to potentially enhance returns and mitigate risks. By actively adjusting asset allocations, investors can adapt to market trends and capitalize on opportunities as they arise.
Challenges of Implementing Dynamic Asset Allocation Strategies
- Requires active monitoring of market conditions
- Can lead to increased trading costs
- Timing the market accurately is challenging
- May result in missed opportunities or suboptimal returns
Tools and Indicators Used in Dynamic Asset Allocation
Some examples of tools and indicators used in dynamic asset allocation include:
- Technical analysis indicators like moving averages and relative strength index (RSI)
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth rates and inflation data
- Market sentiment indicators like the VIX volatility index
- Asset class correlation analysis to identify diversification opportunities
Asset Allocation for Different Goals
When it comes to asset allocation, one size does not fit all. Different investment goals require different strategies to maximize returns and manage risks effectively. Let’s dive into how asset allocation varies based on specific financial objectives and why it’s crucial to align them.
Retirement Planning
For retirement planning, the goal is typically wealth preservation and generating a steady income stream post-retirement. A common strategy is to allocate a larger portion of the portfolio to fixed-income securities like bonds or annuities to ensure stability and reduce volatility in the later years.
Wealth Preservation
When the goal is wealth preservation, the focus shifts to protecting the capital and minimizing losses. This may involve a more conservative asset allocation approach with a higher allocation to cash, bonds, and other low-risk investments to safeguard the principal amount.
Growth
For those seeking growth, the key is to maximize returns over the long term. This usually entails a more aggressive asset allocation strategy with a higher allocation to equities and other high-risk, high-reward investments to capitalize on market opportunities and achieve higher growth potential.
Time Horizon Impact
The time horizon of an investment goal plays a significant role in determining the appropriate asset allocation. Longer time horizons allow for a more aggressive allocation with a higher proportion of equities, as there is more time to recover from market downturns and benefit from the compounding effect of returns over time.