Get ready to dive into the world of mortgage loan rates today, where we unravel the mysteries behind how these rates are determined and what factors influence them. From fixed-rate to adjustable-rate mortgages, we’ve got you covered with all the essential information you need to know.
Stay tuned as we explore the current trends in mortgage loan rates, comparing today’s rates with historical data and shedding light on how economic factors play a crucial role in shaping these rates.
Overview of Mortgage Loan Rates Today
Mortgage loan rates refer to the interest rates that borrowers pay on their home loans. These rates can vary depending on a variety of factors and can have a significant impact on the total cost of the loan over time.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Loan Rates
- The Federal Reserve: The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy can affect mortgage rates. When the Fed raises or lowers interest rates, it can cause mortgage rates to rise or fall accordingly.
- Economic Indicators: Factors such as inflation, unemployment rates, and GDP growth can also influence mortgage rates. A strong economy typically leads to higher mortgage rates.
- Credit Score: Borrowers with higher credit scores are typically offered lower interest rates, as they are considered less risky by lenders.
- Loan Term: The term of the loan, such as 15-year or 30-year, can impact the interest rate. Shorter loan terms often come with lower rates.
- Down Payment: The size of the down payment can affect the interest rate. A larger down payment can result in a lower rate.
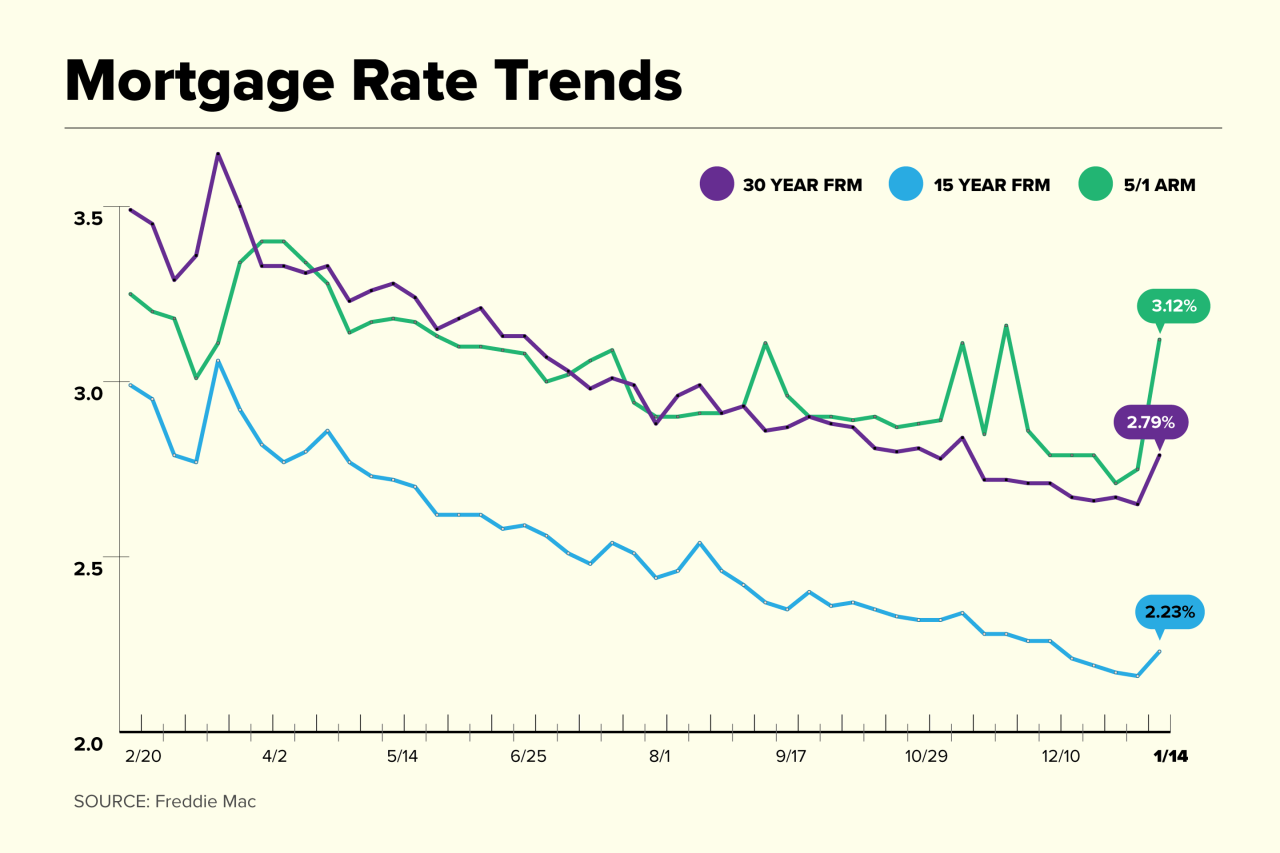
Current Mortgage Loan Rate Trends
In recent months, mortgage loan rates have been experiencing fluctuations due to various economic factors. These trends can impact the affordability of loans for homebuyers and refinancers alike.
Comparison with Historical Trends
- Historically, mortgage loan rates have been influenced by the performance of the economy, inflation rates, and the decisions of the Federal Reserve.
- Today’s rates may be lower or higher compared to previous years, depending on the current economic climate and market conditions.
- It is essential for borrowers to monitor these trends to make informed decisions about when to lock in a rate for their mortgage.
Impact of Economic Factors
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence can influence mortgage loan rates.
- Changes in the stock market, inflation, and global events can also have a significant impact on the direction of mortgage rates.
- The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, including interest rate changes, play a crucial role in shaping mortgage loan rate trends.
Types of Mortgage Loan Rates Available
When it comes to mortgage loan rates, there are different options available for borrowers to choose from based on their financial goals and preferences. The two main types of mortgage loan rates are fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages have a set interest rate that remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that your monthly mortgage payments will also remain constant, providing predictability and stability for budgeting purposes. Fixed-rate mortgages are ideal for borrowers who prefer consistency and want to avoid fluctuations in their monthly payments.
- Pros of Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
- Stable monthly payments for the entire loan term
- Predictable budgeting
- Protection against rising interest rates
- Cons of Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
- Initial interest rates may be higher compared to adjustable-rate mortgages
- Borrowers may miss out on potential savings if market interest rates decrease
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-rate mortgages, also known as variable-rate mortgages, have interest rates that can change periodically based on market conditions. Typically, these loans start with a lower initial interest rate compared to fixed-rate mortgages, but the rate may adjust up or down over time. Borrowers should be prepared for potential fluctuations in their monthly payments.
- Pros of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages:
- Potentially lower initial interest rates
- Borrowers can benefit from falling interest rates
- Cons of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages:
- Monthly payments may increase if interest rates rise
- Less predictability in budgeting due to potential rate adjustments
Factors Influencing Mortgage Loan Rates
When it comes to mortgage loan rates, there are several key factors that can influence how high or low they are. Understanding these factors can help borrowers make informed decisions when looking for a mortgage.
Credit Score Impact
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the mortgage loan rates you qualify for. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine the level of risk they are taking by lending to you. A higher credit score typically results in lower interest rates, as it indicates that you are a responsible borrower who is likely to repay the loan on time. On the other hand, a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates, as lenders may see you as a higher risk borrower.
Housing Market Influence
The overall health of the housing market can also impact mortgage loan rates. In a strong housing market with high demand and increasing home prices, mortgage rates may rise as lenders see less risk in lending money. Conversely, in a weak housing market with low demand and decreasing home prices, mortgage rates may decrease as lenders try to attract borrowers. Economic factors such as employment rates, inflation, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy can also influence mortgage rates.