Get ready to dive deep into the world of handling defaulted loans, where financial institutions navigate the treacherous waters of financial risks and rewards. Brace yourself for a rollercoaster ride filled with strategies, procedures, and the impact of defaulted loans on credit scores.
Now, let’s explore the ins and outs of this vital financial topic.
Importance of Handling Defaulted Loans
When it comes to financial institutions, effectively managing defaulted loans is absolutely crucial. When loans go unpaid, it can have a ripple effect on the lender’s financial health and the overall economy.
Impact on Lender’s Financial Health
Defaulted loans can significantly impact a lender’s financial health by reducing their profits, increasing their operational costs, and tying up resources that could be used elsewhere. This can lead to liquidity issues and even bankruptcy if not managed properly.
Consequences on the Overall Economy
Neglecting defaulted loans can have serious consequences on the overall economy. It can lead to a decrease in lending activities, which in turn can hinder economic growth. Additionally, it can create instability in the financial sector and erode consumer confidence, further exacerbating the situation.
Strategies for Identifying Defaulted Loans
Identifying defaulted loans is crucial for financial institutions to mitigate risks and losses. By implementing effective strategies, institutions can proactively address potential defaulters and prevent loans from defaulting.
Role of Credit Scoring and Analysis
Credit scoring and analysis play a vital role in identifying potential defaulters. Financial institutions utilize credit scores to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers. By analyzing factors such as credit history, debt-to-income ratio, and payment history, institutions can predict the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on a loan. This proactive approach enables institutions to take necessary actions to prevent defaults before they occur.
Early Detection for Prevention
Early detection is key in preventing loans from defaulting. By closely monitoring borrower behavior and financial indicators, institutions can identify red flags that may indicate a borrower is at risk of default. Timely intervention, such as offering financial counseling or restructuring loan terms, can help borrowers overcome financial challenges and avoid defaulting on their loans. Additionally, early detection allows institutions to allocate resources more efficiently and minimize potential losses.
Procedures for Managing Defaulted Loans
When a borrower defaults on a loan, financial institutions must follow specific procedures to recover the funds and mitigate losses. Let’s dive into the steps involved in managing defaulted loans, including legal aspects, regulations, and borrower solutions.
Recovery Process for Defaulted Loans
- Identify the defaulted loan: The first step is to identify loans that are in default by reviewing payment records.
- Notify the borrower: Financial institutions must notify the borrower of the default and provide options for repayment.
- Initiate collection efforts: This involves contacting the borrower to discuss repayment plans and potential solutions.
- Legal action: If necessary, financial institutions may pursue legal action to recover the outstanding debt through court proceedings.
- Recovery of collateral: In cases where the loan is secured by collateral, the financial institution may repossess and sell the collateral to recover the owed amount.
Legal Aspects and Regulations
- Debt collection laws: Financial institutions must comply with federal and state laws governing debt collection practices to protect borrowers from harassment or unfair treatment.
- Loan agreements: The terms and conditions Artikeld in the loan agreement dictate the actions that can be taken in the event of default.
- Regulatory oversight: Regulatory bodies oversee the handling of defaulted loans to ensure compliance with industry standards and consumer protection laws.
Working with Borrowers
- Payment arrangements: Financial institutions may work with borrowers to establish payment arrangements that are feasible based on their financial situation.
- Loan modifications: In some cases, lenders may modify the terms of the loan to make repayment more manageable for the borrower.
- Financial counseling: Offering financial counseling services can help borrowers develop better money management skills and avoid future defaults.
Impact of Defaulted Loans on Credit Scores
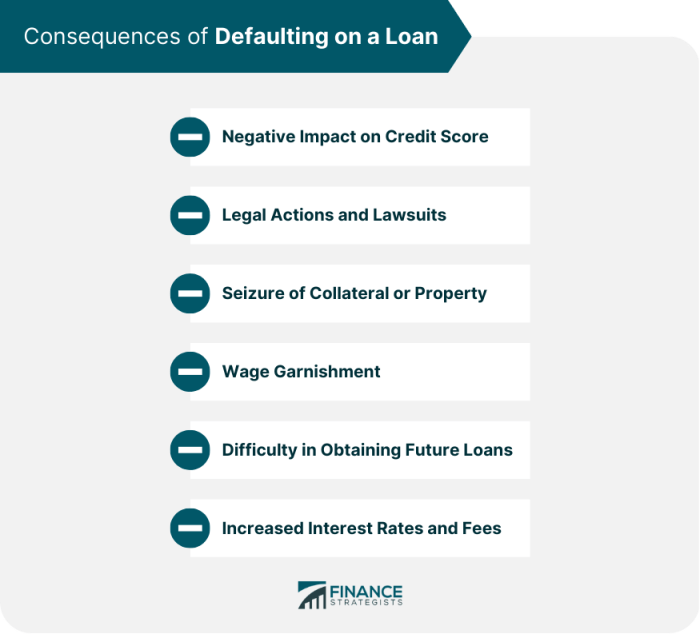
Defaulted loans can have a significant negative impact on an individual’s credit score. When a borrower fails to make loan payments as agreed, it signals to lenders that the borrower is a high credit risk. This can result in a significant drop in the borrower’s credit score, making it more difficult to qualify for credit in the future.
Long-term Consequences of Defaulting on a Loan
Defaulting on a loan can have long-term consequences on one’s creditworthiness. A defaulted loan stays on a borrower’s credit report for several years, typically seven to ten years. During this time, the borrower may face challenges in obtaining new credit, securing favorable interest rates, or even getting approved for housing or rental applications. Additionally, defaulting on a loan can lead to collection efforts, lawsuits, and wage garnishment, further damaging the borrower’s financial stability.
Rebuilding Credit After Defaulting on a Loan
Rebuilding credit after defaulting on a loan is possible but requires time and effort. Borrowers can take steps to improve their credit score by making timely payments on any remaining debts, reducing overall debt levels, and establishing a positive payment history. Additionally, borrowers can consider obtaining a secured credit card, becoming an authorized user on someone else’s credit card, or working with a credit counselor to develop a personalized credit improvement plan. By demonstrating responsible financial behavior over time, borrowers can gradually rebuild their credit and improve their creditworthiness.